Ошибка grub rescue unknown filesystem
Содержание:
- When Error No Such Partition Grub Rescue Windows 10 Happens?
- To fix grub rescue go with following steps:
- Что такое менеджер загрузки?
- Восстановление Grub2 с помощью LiveCD
- Features
- Монтирование разделов
- How do I fix error no such partition grub rescue on Windows 10?
- Удаляем Grub
- About «Error No Such Partition. Grub Rescue»
- Генерация файла конфигурации GRUB
- Entering rescue mode
- Search & Set
- grub rescue>
When Error No Such Partition Grub Rescue Windows 10 Happens?
Suppose that there are two systems, Windows 10 & Ubuntu and you may want to do some disk and partition operations to these two operating system partitions on the same hard disk; this is when the problem would occur. (Especially to Ubuntu OS partition)
1. Delete Ubuntu Partition
There are times when you don’t like such a system because you think the command line based system is too difficult to use. You then want to uninstall it in order to create a new partition. However, sometimes disk space is very limited, and then you would decide to delete such a partition to free up some disk space and expand other partitions.
2. Resize/Merge/Split Partition
When you manage your hard drive and do operations such as resize/merge/split Ubuntu partition, this issue may appear during the process when restarting computers.
3. Reinstall Ubuntu OS
Sometimes, you will reinstall the Ubuntu operating system for reasons including system breakdown, or system file damage.
4. Restore Ubuntu OS to the Old Version
After installing an update, some issues or errors will appear which leads to you choosing to restore Ubuntu OS to the old Version, for example, Ubuntu 8.X.
To fix grub rescue go with following steps:
First thing is we have to start our OS only then after we can fix grub.
#to start OS—>
error: unknown filesystem.
Entering rescue mode…
grub rescue>
When you see such an error first we have to check for “Filesystem” is ext2′
grub rescue> ls # type ‘ls’ and hit enter to see drive partition.
(hd0) (hd0,msdos6) (hd0,msdos5) (hd0,msdos4) … # you will see such things
this are our drives now we have to check which one is ext2.
go for another drives until you get “Filesystem is ext2”.
now set the path
Now just fix grub by following command on any Ubuntu
sudo grub-install /dev/sda
sudo apt-get update
# to update grub
sudo apt-get upgrade
make sure you must update grub after login into OS
Что такое менеджер загрузки?
Менеджер загрузки — это программа, которая располагается в начальных секторах диска, т.е. в MBR (Master Boot Record — Главная загрузочная запись) жесткого диска. После проверки системы в ходе загрузки, BIOS (Basic Input/Output System), передаёт управление MBR, если система настроена на загрузку отсюда. Затем выполняется программа расположенная в MBR. Эта программа называется менеджером загрузки. Её задача — передать управление операционной системе, которая продолжит процесс загрузки.
Существует множество менеджеров загрузки, включая GNU GRUB (Grand Unified Boot Loader), Bootmanager, LILO (LInux LOader), NTLDR (менеджер загрузки для систем на базе Windows NT), и т.д. Я решил обсудить GNU GRUB и его использование.
Что такое GRUB?
GRUB — это очень мощный менеджер загрузки, который может загружать множество операционных систем, таких как Windows, DOS, Linux, GNU Hurd, *BSD и т.д.
В настоящий момент LILO является самым популярным менеджером загрузки, используемым практически всеми, кто работает с несколькими операционными системами. Но если вы используете LILO, вы должны помнить, что необходимо перезапускать LILO каждый раз как вы изменяете вашу конфигурацию или устанавливаете новое ядро. Также, LILO обладает меньшей гибкостью, чем GRUB.
GRUB — синоним слова гибкость. Его последний релиз, 0.5.96.1, поддерживает ext2 ( файловую систему, используемую Линукс), FAT16 и FAT32 (используемые Win9x и ME), FFS (Fast File System (Быстрая файловая система) используемую *BSD UNIX), ReiserFS (новую журналируемую файловую систему, разработанную для Линукс и интегрированную в ядро Линукс 2.4.1), и minix (старую файловую систему, разработанную для ОС MINIX, также используемую ранними версиями Линукс). С GRUB, вы можете «заглянуть» внутрь этих файловых систем, даже не загружая операционной системы. Например, если вы хотите увидеть дату и время, сохранённые в текстовом файле, и у вас нет времени на загрузку всей операционной системы, вы можете использовать командную оболочку GRUB (строка с подсказкой «grub>») ,введите:
grub> cat (номер раздела)/home/god/filename.txt.
Вы увидете всё содержимое текстового файла, включая даты и время. Лучшее свойство GRUB — то, что вы можете загрузить любое ядро на любом разделе, прямо в ходе начальной загрузки. Например, если вы забыли добавить только что скомпилированное ядро в список, вам скорее всего потребуется загрузиться, добавить его в список и затем перезагрузиться, чтобы использовать его. Но с GRUB, вы можете просто использовать командную оболочку и загрузить при помощи её желаемое изображение ядра.
Теперь я опишу три основных шага, которые необходимо выполнить, чтобы начать использовать GRUB: компиляция, установка и конфигурирование.
Восстановление Grub2 с помощью LiveCD
В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как выполняется восстановление Grub2 обоими способами. Начнем с более простого способа — с помощью LiveCD. Хотя и статья ориентирована на Linux Mint, но на самом деле подойдет абсолютно для любого дистрибутива, потому что во всех дистрибутивах загрузчик один и тот же, и команды такие же, только версии могут немного отличаться.
Начнем с того, что вам нужна LiveCD система, той же разрядности, что и ваша система Linux Mint, на которую был установлен Grub
Причем, неважно будет там графический интерфейс или нет. Обычно все необходимые инструменты поддерживаются всеми дистрибутивами
А нужны нам только утилиты fdisk, mount и chroot. Чтобы восстановить загрузчик grub2 просто следуйте описанным ниже шагам.
Шаг 1. Загрузка LiveCD
Сначала вставьте носитель с LiveCD системой в дисковод или порт USB, если это флешка. Для загрузки с носителя, возможно, вам сначала понадобится зайти в меню BIOS и выставить приоритет загрузки с внешнего устройства.
Для запуска BIOS нажмите Del, F2, F8 или Shift +F2. В открывшимся меню найдите раздел Boot, и в пункте Boot Device Priority или 1st Boot Device или Boot Option #1 выберите нужное устройство:
Дальше перейдите на вкладку Exit и выберите Exit & Save settings. Дальше начнется загрузка образа.
Шаг 2. Определение разделов
Перед тем как восстановить Grub2, нам нужно понять — на каком разделе установлена система, и на каком разделе были или должны быть файлы загрузчика. Самый простой способ это сделать — воспользоваться утилитой fdisk.
В выводе программы вы видите — разделы всех подключённых к компьютеру дисков, их размер, а также файловую систему. По этим данным вам и предстоит понять, какой раздел используется в качестве корня в вашей системе. Если вы делали разметку вручную, вам не составит труда понять где то, что нужно. Например, у меня корень — /dev/nvme0n1p5 — размером 37 гигабайт, а для загрузчика отдельный раздел не выделялся. Но обычно он тоже имеет файловую систему ext4 ил ext2, а размер до 500 мегабайт. В случае с обычным SSD или HDD диском имя раздела будет начинаться с /dev/sd*. Например: /dev/sda или /dev/sdb и так далее
Шаг 3. Монтирование файловой системы
Теперь вам предстоит смонтировать вашу корневую файловую систему в каталог /mnt:
Кроме того нужно смонтировать раздел boot. Например, если бы он у меня находился по адресу /dev/nvme0n1p1:
Шаг 4. Подготовка к входу в систему
Чтобы восстановить загрузчик Linux мы будем использовать вашу основную систему Linux, запущенную на ядре от LiveCD. Такую возможность предоставляет команда chroot. Но перед тем, как ее использовать нужно вручную подключить к вашей корневой ФС, смонтированной в /mnt все необходимые файловые системы взаимодействия с ядром — /dev, /sys, /proc:
Шаг 5. Вход в окружение системы
Для входа в окружение вашей системы используйте команду:
Первый параметр указывает папку, в которую была смонтирована корневая файловая система, а второй — оболочка, используемая для интерпретации команд пользователя.
Затем выполните эти команды для загрузки и обновления переменных профиля:
Теперь вы находитесь в Linux Mint, и можете выполнять почти все его программы, разумеется, недоступны сервисы, поскольку во время загрузки не использовалась система инициализации, а также как следствие, недоступно графическое окружение.
Шаг 6. Восстановление Grub2
Теперь восстановление Grub в Linux Mint. Просто выполните следующие команды. Первая, для переустановки загрузчика на жесткий диск:
Здесь /dev/sd* — имя вашего жесткого диска.
Теперь создадим новый конфигурационный файл:
Путь к конфигурационному файлу может немного отличаться, так что будьте внимательны.
Еще можно использовать команду:
Но она работает только в Ubuntu и основанных на ней дистрибутивах.
Features
Rescatux 0.73 supports booting from UEFI Secure Boot and traditional BIOS. Both amd64 and 686 systems are supported.
Rescatux
includes Rescapp, a graphical rescue tool that will assist users to
regain access to a computer that has become non-bootable among many
other features.
GNU/Linux options
- Change Gnu/Linux Password : Change a user’s password
- File System Check (Forced Fix) : File System Check (Forced Fix)
- Easy GNU/Linux Boot Fix : Fsck partition, update grub menues, restore GRUB into the MBR and order UEFI entries
- Restore Grub : Restore GRUB into the MBR
- Regenerate sudoers file : Define a new sudoers file
- Update Grub Menus : Update GRUB Configuration File
UEFI Boot specific options
- UEFI Partition Status : Check UEFI partition status
- Check UEFI Boot : Check if Rescatux has boot in UEFI mode
- Create UEFI Boot Entry : Create a new UEFI Boot entry out of your EFI files
- Change UEFI Boot Order : Change UEFI Boot order
- Reinstall Microsoft Windows UEFI : Reinstall Microsoft Windows UEFI boot entries
- Fake Microsoft Windows UEFI : Fake Microsoft Windows UEFI boot entry
- Hide Microsoft Windows UEFI : Hide Microsoft Windows UEFI boot entry and define default fallback one.
- Easy Windows Admin : Promote to Admin, Reset Windows (NT,200x,XP,Vista,Seven) password and unlock user
- Reset Windows password : Reset Windows (NT,200x,XP,Vista,Seven,10) password
- Promote Windows user to Admin : Promote Windows (NT,200x,XP,Vista,Seven,10) user to Administrator
- Unlock Windows user : Unlock Windows (NT,200x,XP,Vista,Seven,10) user
Other options
- Boot Info Script : Boot Information Script
- Check bios_grub partition on GPT : Check if there is a bios_grub partition on a GPT disk
- Gptsync : Create an hybrid MBR inside a GPT partition (Gptsync)
- Recompute Hybrid GPT/MBR CHS : Recompute CHS values on an hybrid GPT/MBR partitiont table
- Restore Windows MBR : Restore generic MBR code so that Windows boots again
- System Info Script (Inxi) : System Info Script (Inxi)
Support features
- Chat : Get online human help (chat)
- Help : Help on using Rescapp
- Share log : Share Rescatux logs. It generates a pastebin in paste.debian.net and shows it to you so that you can copy and paste the url in the chat.
- Share log on forum : Share Rescatux logs on a forum. It generates a temporary file ready to copy and paste on your favourite forum (ubuntuforums.org and others).
- Show log : Show Rescatux logs so that you can ask help and supporters can know what happens when you run Rescatux options
- Web : Access online Rescatux website
External tools
- Gparted : GParted is a free partition editor for graphically managing your disk partitions.
- Testdisk : Testdisk is a text wizard drive program for rescuing disks, partitions, and files.
- Photorec : Photorec is a text wizard drive program for rescuing files. Despite its name it recovers much more files than photo files.
Монтирование разделов
Примонтируем корневой раздел. Выполняем команду (вместо /dev/sda2 вы должны указать свой раздел):
Мы примонтировали раздел /dev/sda2 в директорию /mnt .

Если для загрузчика у вас выделен отдельный раздел, то нужно примонтировать еще и его (вместо /dev/sdX укажите ваш boot-раздел):
Теперь можно посмотреть содержимое директории /mnt , чтобы убедиться, что мы примонтировали верный раздел:
Вывод команды должен быть примерно следующим
Обратите внимание есть ли в этом списке каталог /boot , так как именно в нем установлен GRUB

Также можно проверить, что директория boot не пустая:
У меня вывод команды выглядит следующим образом
Обратите внимание на присутствие каталога с именем grub

Далее нужно создать ссылки на несколько директорий, к которым GRUB должен иметь доступ для обнаружения всех операционных систем. Для этого выполните команды:
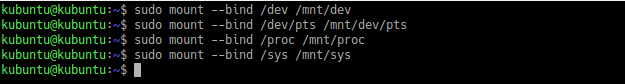
Монтирование EFI-раздела
Если у вас используется UEFI, то еще нужно примонтировать EFI-раздел в директорию /mnt/boot/efi (выше я указал пример вывода команды fdisk -l в котором показан EFI-раздел):
How do I fix error no such partition grub rescue on Windows 10?
Error no such partition entering rescue mode grub rescue is common after Ubuntu Linux is removed from dual boot PC. The error occurs mainly out of misconfigured bootloader or wrong active partition. To fix no such partition error, go to the first part, you have Windows installation or repair disc; otherwise, refer to the second part.
Part 1 Fix no such partition with Windows installation/repair disc
With Windows 10 installation/repair disc, you can run Startup Repair or go to Command Prompt to repair Windows 10.
Run Startup Repair
Step 1. Insert the Windows 10 installation CD/DVD in your computer.
Step 2. Reboot the PC; press a functional key to enter BIOS and boot from the installation disc.
Step 3. Choose a language, a time, a currency and a keyboard or another input way. Then, click “Next”.
Step 4. In this windows, click “Repair your computer”.
Step 5. In Choose an option window, choose Troubleshoot.
Step 6. Choose “Advanced options” and “Startup Repair”.
Then, wait patiently for Windows automatic repair to complete.
Access Command Prompt to fix the error manually
When Startup Repair not working, you can go to Command Prompt (Boot from Windows 10 installation disc, go to “Repair your computer” > “Troubleshoot” > “Advanced options > Command Prompt” and run commands to fix bootloader or set active partition.
① Rebuild BCD
-
bootrec /fixmbr
-
bootrec /fixboot
-
bootrec /rebuildbc
② Restore boot sector code
-
diskpart
-
list volume
Here all volumes will be listed, locate the Windows installation CD/DVD and keep the drive letter of it in mind.
-
exit
-
: cd boot dir
-
bootsect /nt60 SYS /mbr
-
exit
Then, you can remove the CD/DVD from the disk tray and reboot the PC to see if the error no such partition grub error resolved.
③ Set active partition
Or you can set right partition as active from Command Prompt to fix the error. The commands are given below:
-
diskpart
-
list part
-
select partition x
-
active
-
exit
Then, disconnect the Windows 10 installation disc and restart your computer to check whether no such error disappear.
Part 2. Fix no such partition with a bootable USB drive
If Startup Repair or Command Prompt is not available as you don’t have Windows installation or repair disc, it’s time to employ a third-party bootable USB creator, AOMEI Partition Assistant Standard to repair boot failure for Windows 10. Free download it on a working PC and Then, insert the bootable USB into the PC that’s stuck in no such partition grub rescue issue, boot the PC from the USB drive and repair OS.
Download Freeware
Win 10/8.1/8/7/XP
Secure Download
Step 1. After booting from the bootable USB drive successfully, you’ll in the main interface of AOMEI Partition Assistant Standard. Right click the system hard drive and choose “Rebuild MBR”.
Step 2. Choose a type for MBR based on the current OS of the hard drive.
Step 3. Click “Apply” and “Proceed” to execute the operation.
Note: AOMEI Partition Assistant has many other fuancitons available, such as surface test, check/ repair bad sector and so on.
Удаляем Grub
Некоторые юзеры затрудняются в вопросе, как удалить Grub, так как он подменяет собой стандартный загрузчик, и при удалении Linux перестают загружаться также и оставшиеся операционные системы. Хотя сам процесс несложный, применимы различные способы, зависящие от установленной второй системы.
Удаление при установленной Windows XP
Если на ПК стоит Windows XP, проблема, как удалить Grub, решается не так быстро, но без особых сложностей. Запустите менеджер жёсткого диска, который удалит программные компоненты, отмеченные ext. Хорошо подходит для процедуры удаления Power Quest PartitionMagic 8.0. Затем вам потребуется восстановление загрузчика Windows для работы ПК после удаления Linux. Действуйте по алгоритму.
С помощью утилиты удалите разделы с меткой ext
- Внизу окна приложения цветовое обозначение разделов. Удалив эксплуатируемые Linux, освободите место, оно выделится серым.
- Умная машина станет перезагружаться, высветится сообщение: «NTLDR is missing». Оно говорит, что система не может запустить ОС Windows, требуется восстановить файлы.
- Запустите консоль восстановления и подключите компакт-диск либо загрузочную флешку.
- Консоль запросит указать, в какую копию ОС следует войти. Ставьте «1».
- У вас запросят пароль администратора, введите его.
- Затем введите команду fixmbr, восстанавливающую таблицы разделов, перезаписывающую загрузочную область.
- Консоль выведет предупреждение и запросит подтверждения процесса, введите «Y».
- Загрузочная область создаётся, введите затем команду fixboot для записи загрузочного сектора на основной диск.
- Подтвердите по запросу операцию, набрав «Y».
Компьютер перезагрузится, восстановление загрузчика будет успешно завершено, запустится Windows XP.
Удаление при установленных Windows 7, 8
Процедура при установленных Windows 7-8 проще, чем вышеописанная. В данном случае вам не понадобятся загрузочные флешки, запуск консоли. Действуйте по алгоритму:
- Заходите в «Пуск» — «Выполнить».
- В поле окна открытия утилит впишите list disk, нажмите Enter, после чего увидите список устройств, имеющихся у вашего ПК.
- Впишите «select disk №…», указав номер диска с установленным Grub.
- Нажмите Enter. Выйдет сообщение о выборе диска.
- Вбейте команду «clean» — «Enter».
- Появится сообщение об успешной очистке диска.
Если вы уже удалили Linux, то Windows не сможет загрузиться. Поэтому нужен установочный диск или флешка с системой. Настройте BIOS на загрузку с нужного устройства и загрузитесь с диска или флешки. Вместо установки выберите восстановление системы, а затем командную строку. В этой строке введите поочередно такие команды:
- EXE /FixBoot
- BOOTREC.EXE /FixMBR
После этого файловая система будет исправлена и в загрузочном секторе появится запись, что компьютер должен загружаться с системы Windows. Собственно, этот же процесс происходит при новой установке системы, но теперь вы вместо этого только исправили загрузчик.
Удаление при FreeDos
При установленной FreeDos программу-загрузчик удалить возможно посредством командной строки. Вы просто форматируете диск с загрузочной областью.
- Запустите командную строку.
- Просмотрите содержание дисков, дав команду «dir».
- Обнаружив загрузочный сектор, отформатируйте весь раздел, вбив команду «format» и указав на этой же строчке нужный диск, например, «с:».
- После выполнения процедуры Grub будет убран с жёсткого диска.
Удаление Grub4Dos
Если у вас установлен загрузчик Grub4Dos, его удалить легко через командную строку. Набираете там команду «sudo apt-get purge grub2 grub-pc», и Grub удалит себя. Далее с помощью загрузочного диска, специальной консоли выполняете восстановление загрузчика, запуск имеющейся ОС.
Хотя Linux имеет много преимуществ перед другими системами, часто выбирают современные ОС либо устанавливают две системы. Но переходы между ними затруднены, возникают конфликты в программном обеспечении, и приходится удалять такой привычный, удобный Linux. Выше мы подробно описали, каким образом выполнить удаление, не нарушив работы второй системы. Теперь вы сможете, удалив Grub, оставить на ПК только одну ОС; знаете, как восстановить загрузчик Windows. Внимательно выполняйте операции, действуйте по руководству, прилагаемому к загрузчику, и вы успешно сделаете всё необходимое.
About «Error No Such Partition. Grub Rescue»
«I was dual-booting Windows 10 and Linux Ubuntu on my desktop. Since the system was unable to detect Ubuntu in the initial menu that appears on rebooting, I deleted the partition onto which I had installed Ubuntu while in Windows 10. I then installed PowerISO, which prompted me to reboot the system. Now, however, it led me to the grub rescue prompt and said, «no such partition. Grub rescue>», How can I fix no such partition grub rescue Windows 10?»
No such partition is a common error that usually occurs in Windows & Ubuntu dual boot system. It always appears when you intend to boot your computer but get stuck at the boot screen with the following error messages:
Example 1:
error: no such partition.
grub rescue>
Example 2:
error: no such partition.
Entering rescue mode…
grub rescue>
Генерация файла конфигурации GRUB
Данный шаг нужно выполнять не всем. Если у вас был установлен GRUB и вы уверены, что его конфигурация верная, то можно перейти к следующему шагу.
Для генерации файла конфигурации GRUB используется команда update-grub . Данная команда автоматически определяет файловые системы на вашем компьютере и генерирует новый файл конфигурации. Выполняем команду:
В выводе команды будет показано, какие операционные системы были найдены.

Если вдруг утилита update-grub не определила ваш Windows (у меня такое было для UEFI), то можно будет запустить update-grub повторно уже из вашей Linux-системы, когда вы в нее загрузитесь (мне это помогло и Windows определился).
Entering rescue mode
Итак, в случае проблем с загрузкой Ubuntu вы можете оказаться в режиме grub rescue.
Machine UUID... Booting from Hard Disk... error: no such partition. Entering rescue mode... grub rescue>
Это может символизировать как простую ошибку, которую легко исправить, так и серьезные проблемы. Рассказываю, что нужно делать в таком случае и как починить загрузку системы.
Первым делом запускаем команду ls и смотрим, какие разделы у нас доступны.
> ls (hd0) (hd0,gpt3)
В моем случае доступен только один 3-й раздел, скорее всего корневой. Раздела /boot, который обычно 1-й или 2-й нет. Проверим это наверняка. Смотрим содержимое доступного раздела:
> ls (hd0,gpt3)/
По содержимому раздела видно, что это корневой. Самого раздела /boot, с которого должна начинаться загрузка ubuntu тут не видно. Если его никто специально не удалял и не затирал, то он пропал в результате какого-то сбоя или ошибки. Можно попробовать это исправить. Сделаем это отдельно ниже, а пока рассмотрим случай, когда boot раздел тут все же присутствует и имеет имя, к примеру, (hd0,gpt2). Тогда там же в консоли grub продолжаем.
> set prefix=(hd0,gpt2)/grub > set root=(hd0,gpt2)
Далее загружаем некоторые модули. Какие будут нужны, точно не известно и зависит от типов разделов диска. Показываю самые популярные:
> insmod ext2 > insmod lvm > insmod part_msdos
Можно для начала попробовать вообще без модулей, а потом добавлять по одному. В самом конце загружаем модуль normal.
> insmod normal > normal
После этого у вас должно открыться стандартное меню загрузки Ubuntu. Если это так, то вам повезло. Дальше загрузится система. Вам нужно будет в нее зайти и далее перейти в раздел по восстановлению grub в этой статье. Получилось так, что у вас сам загрузочный раздел жив, но сбились его настройки, поэтому он сам не смог загрузить основную систему. Это не трудно исправить и ниже я показываю как.
Search & Set
A great many boot problems are due to incorrect paths to required files. The GRUB 2 terminal, in either ‘failure’ mode, provides a robust ability to search hard drive(s) and partitions and to inspect their contents.
In order to boot successfully, the root, prefix, linux and initrd variables must be correct. The user must verify the paths and names of these items. If they are incorrect, use the commands below to find and fix them. GRUB 2 variable settings can be viewed with the set command.
In the following examples, X is a hard drive number; Y is a partition number. If a command example includes either of these replace them with the appropriate value.
How & Where to Search
In the graphic below, the text in red are commands to be entered by the user, and text in green is the output of the command on an operating system (i.e. what you would like to see if your Ubuntu installation is on sda1).
-
The first hard drive is . The first partition is 1. Thus sda1 becomes (hd0,1), sdb5 is (hd1,5).
-
Use the ls command in the follow manner
- «Tab completion» may work — enter part of the filename and press the TAB key.
|
Command |
Purpose |
|
ls |
Search the entire computer for devices and partitions: (hd0) (hd1) (hd0,1) (hd0,5) (hd1,1) |
|
ls / |
Search the root directory of the device designated as root (use the set command to check root). |
|
ls (hdX,Y) |
View information about a partition — format, size, UUID, etc. |
|
ls (hdX,Y)/ |
View the root contents of a partition. Use this command to look for the presence of vmlinuz and initrd.img symlinks |
|
ls (hdX,Y)/boot/ |
View the contents of a folder |
|
ls (hdX,Y)/boot/ |
Inspect the /boot folder. It should contain the actual kernel (linux-3.2…) and initrd image (initrd.img-3.2….) |
|
ls (hdX,Y)/boot/grub/ |
Inspect the /boot/grub folder. It should contain grub.cfg and many *.mod files. If looking for a specific file, include the name in the search to limit the number of returns. If available, the command set pager=1 will also limit returns to a single screen. |
|
What to Look For |
Where It Should Be (Default Installation) |
Specific / General Search Example |
|
grub.cfg |
(hdX,Y)/boot/grub/ or /boot/grub/ |
ls (hdX,Y)/boot/grub/grub.cfg or ls /boot/grub/ |
|
vmlinuz |
(hdX,Y)/ or |
ls (hdX,Y)/vmlinuz or ls /vmlinuz or ls / |
|
linux-3.2.0-14* |
(hdX,Y)/boot/ or /boot/ |
ls (hdX,Y)/boot/vmlinuz-3.2.0-14 |
|
initrd |
(hdX,Y)/ or |
ls (hdX,Y)/ or ls /initrd |
|
initrd.img-3.20-14 |
(hdX,Y)/ or /boot/ |
ls (hdX,Y)/boot/initrd.img-3.20-14 or ls (hdX,Y)/boot/ |
* Note: Use the full kernel name, including -generic, when searching or setting a kernel variable. Using the «TAB completion» technique may eliminate some typing and be more accurate if available.
Use the following commands to set these parameters (if incorrect). Substitute the correct value for X and Y. (Example: set root=(hdX,Y) becomes set root=(hd0,5) )
|
Task |
Command |
Notes |
|
Set the prefix |
set prefix=(hdX,Y)/boot/grub |
Use the actual location of the grub folder |
|
Set root |
set root=(hdX,Y) |
|
|
Set the kernel |
linux /vmlinuz root=/dev/sda1 ro |
Set the kernel if the symlink vmlinuz exists in / |
|
Set the kernel |
linux (hdX,Y)/boot/vmlinuz-3.0.2-14 root=/dev/sda1 ro |
Set the kernel itself |
|
Set the initrd image |
initrd /initrd.img |
Set the initrd image if the symlink exists in / |
|
Set the initrd image |
initrd (hdX,Y)/boot/initrd.img-3.0.2-14 |
Set the initrd image itself |
The commands which follow assume you have determined the proper parameters for prefix, root, linux, and initrd. Review the section of this page for guidance .
grub rescue>
The GRUB 2 rescue mode is a major enhancement to the GRUB bootloader. The presence of the grub rescue> prompt signifies that GRUB 2 has failed to find the grub folder, the grub.cfg file, and/or the associated modules. The rescue prompt is presented so the user can provide the path to the grub folder, load the necessary modules, and provide the proper boot commands.
A common reason for the grub rescue> prompt is an incorrect path to the grub folder. Reasons for the prompt also include a failure to update GRUB 2 after certain system or partition operations, improper designation of the grub folder location, missing linux or initrd.img symlinks in /, or a failed installation.
To successfully boot from the grub rescue> prompt:
-
The grub folder must exist and contain the necessary GRUB 2 files and modules.
-
The proper paths must be set via the set prefix command.
Many GRUB 2 commands will not work until the correct path is set. If the path to the grub folder (normally /boot/grub) is not correct, an unknown command or file not found message is likely.
- The necessary modules must be loaded.
The kernel cannot be loaded until the ‘linux’ module is loaded.
- A Linux kernel and initrd.img must be located and loaded.
Use the section to locate the correct partitions and file locations. Once the user has confirmed the paths and existence of the proper folders using the section, run the following commands:
|
1. set prefix=(hdX,Y)/boot/grub |
Use the values determined earlier. |
|
Example: If the Ubuntu system is on sda5, enter: set prefix=(hd0,5)/boot/grub |
|
|
2.* set root=(hdX,Y) |
Confirm the correct X,Y values and press ENTER. |
|
Example: If the Ubuntu system is on sda5, enter: set root=(hd0,5) |
|
|
3. insmod normal |
Load the normal module. |
|
If the module loads there will be no message. |
|
|
If the module fails to load, try the full path: insmod (hdX,Y)/boot/grub/normal.mod |
|
|
4. normal |
Transition to the normal GRUB 2 mode with increased functionality. |
|
If the module loads there will be no message. |
|
|
If the module loads, HELP, TAB completion and command recall using the UP/DN keys should be available. |
|
|
5. set |
(Optional) Review the current settings. |
|
6. insmod linux |
Load the linux module. An error message usually means the path is incorrect. |
|
7.* linux /vmlinuz root=/dev/sdXY ro |
Selects the latest kernel. |
|
Example: linux /vmlinuz root=/dev/sda5 ro |
|
|
If the vmlinuz symlink does not exist in /, use the full path to the kernel in /boot |
|
|
Example: linux /boot/vmlinuz-3.2.0-14-generic root=/dev/sda1 ro |
|
|
8. initrd /initrd.img |
Selects the latest initrd image. |
|
If the initrd symlink does not exist in /, use the full path to the initrd image in /boot |
|
|
If successful, after ENTER there will be a slight delay and no messages. |
|
|
9. boot |
Boot to the latest kernel on the selected partition. |
* Wubi users only — substitute these commands in Steps 2 and 7:
1.set root=(loop0)
2. linux /vmlinuz root=/dev/sdXY loop=/ubuntu/disks/root.disk ro
Some additional considerations:
-
The current prefix and root settings may be checked at any time with the set command. To remove a setting, use the unset command.
Example: unset prefix
-
Modules must be loaded before they can be used. If a module has not been loaded a unknown command error is displayed. If an incorrect path is specified, a file not found error message may be displayed.
-
The linux module must be loaded to be able to load both the kernel and the initrd image unless the normal module is loaded first.
-
If the modules cannot be found in the /boot/grub folder, the user may be able to load them from the /usr/lib/grub/i386-pc folder. The address if Ubuntu was installed on sda1 would be (hd0,1)/usr/lib/grub/i386-pc and the command would be:
insmod (hd0,1)/usr/lib/grub/i386-pc/normal.mod
Refer to the section if the system successfully boots.